When an engine with coil-on-plug (COP) ignition starts to misfire, there are two challenges: finding out which cylinder is misfiring and finding out why. Even if you find a bad coil, simply replacing it is not the whole repair, because like so many other parts of a vehicle, COP ignition coils don't really die, they're murdered. We'll discuss how and why later; first let's focus on. Enable dwell control and adjust as needed to match the coils you are using. Set the dwell at a very low value to start with (we've found Ford EDIS coils have especially short dwell times) and increase it slowly. Back it off if the BIP373s become hot to the touch. The instructions below work for either MS2 B&G code or MS2/Extra.
General description
An ignition system is a system for igniting a air-fuel mixture. Ignition systems are well known in the field of internal combustion engines such as those used in petrol (gasoline) engines used to power the majority of motor vehicles. Ignition system is divided into two electrical circuits - the primary and secondary circuits. The secondary circuit consists of the secondary windings in the coil, the high tension lead between the distributor and the coil (commonly called the coil wire) on external coil distributors, the distributor cap, the distributor rotor, the spark plug leads and the spark plugs.
Principle of operation of the secondary ignition circuit
The coil is the heart of the ignition system. Essentially, it is nothing more than a transformer which takes 12 volts from the battery and increases it to a point where it will fire the spark plug as much as 40,000 volts. The term 'coil' is perhaps a misnomer since there are actually two coils of wire wound about an iron core. These coils are insulated from each other and the whole assembly is enclosed in an oil-filled case. The primary coil, which consists of relatively few turns of heavy wire, is connected to the two primary terminals located on top of the coil. The secondary coil consists of many turns of fine wire. It is connected to the high-tension connection on top of the coil.
Ignition systems can be divided into the following types:
- Distributor Ignition System
- Direct Ignition System (DI)
- Coil-on-Plug (COP) type – individual coil for each cylinder and the coil pack is mounted directly over the spark plugs.
- Individual coil for each cylinder with separate HT (high tension) leads.
- DIS-Wasted Spark Ignition - separate coil for each two cylinders.
Synchronous ignition with two secondary winding coil terminals.
Distributor Ignition
The distributor ignition system is the most common ignition system for early model year vehicles. Distributor ignition systems use one coil that fires one spark plug at a time on the compression stroke only. Viewing the primary ignition pattern requires that you have to monitor the voltage signal on the negative side of the coil's primary circuit and to identify the trigger cylinder by using the RPM probe.
The classical or conventional ignition system consists of the following components: ignition coil, distributor, spark plugs, high-voltage wires and some means of controlling the primary ignition circuit. The primary circuit of the ignition coil can contain: points, points controlling a transistor, the transistor being controlled by some other means (breaker less) or electronic ignition. In point-type ignition systems the current in the primary circuit is controlled by a mechanical switch (or breaker). The mechanical points may control a switching transistor which opens and closes the primary circuit of the ignition coil. In breaker less transistor and electronic ignition a Hall effect, VRS (Variable Reluctance Sensor) or an optical sensor may be used to control the switching transistor.
Current flows from the positive terminal of the battery, through the ignition switch and/or relay, through a fuse and on to the positive terminal of the ignition coil. The current returns to the battery through the negative terminal of the ignition coil, on through the switching device (points or a transistor) through the vehicle chassis, and to the negative terminal of the battery. While current is flowing in the primary circuit a magnetic field builds up in the ignition coil. Due to the inductance of the ignition coil it takes some time (1-6 mS, depending on design) for the primary current to reach its nominal value. When the primary current flow is interrupted, the magnetic field collapses rapidly (in about 20µS) and a high voltage is induced in the primary winding (CEMF Counter electro motive Force). This voltage is transformed in to a very high voltage in the secondary winding. The amplitude of this voltage depends on the turns ratio (commonly 100:1). A 300V primary voltage, therefore, will be 30 000V in the secondary winding. The voltage will only build until the break down voltage of the spark gap is reached - the firing voltage of the spark plug.
Direct Ignition System (DI)
COP systems use one individual coil for each spark plug. Each coil is located directly on top of its spark plug and does not use any external spark plug wires. Each coil pack also has an independent primary circuit which must be tested individually.
The individual ignition coil by one running cycle of the engine generates one ignition spark. Therefore, in individual ignition systems is required synchronization of coils work with position of a camshaft.
At submission of the voltage to the primary coil, the current starts to flow by a primary coil and because of that in the core of the coil changes the value of the magnetic flux. Change of the magnetic flux value in the core of the coil leads to occurrence of the voltage of positive polarity on a secondary coil. Because the speed of increasing of the current in the primary coil is slow, the voltage arising on a secondary coil is small – according 1…2 kV. But in the certain conditions the voltage value can be sufficient for untimely occurrence of the spark between electrodes of a spark plug and as consequence, too early ignition of the air/fuel mixture. In order to prevent possible damages of the engine due to untimely occurrence of the spark, formation of the spark between electrodes of a spark plug at submission of a voltage to a primary coil should be excluded. In the individual ignition systems, occurrence of this spark is prevented by means of built-in diode EFU to the ignition coil switched consistently in a circuit of a secondary coil.
At the moment of closing of the output ignition cascade, current in the primary circuit sharply interrupts, and the magnetic flux promptly decreases. This fast change of the magnetic flux value is causes to occurrence of the high voltage on a secondary coil of the ignition coil (under certain conditions, the voltage on a secondary coil of the ignition coil can achieve 40…50 kV). When this voltage achieves the value providing formation of the spark between electrodes of a spark plug, the compressed in the cylinder air/fuel mixture is ignited from the spark between electrodes of a spark plug.
In some systems coils are not located directly on top of each spark plug and external spark plug HT leads are used.
Each coil pack also has an independent primary circuit which must be tested individually.
DIS-Wasted Spark Ignition
DIS ignition systems use one coil for every two cylinders, also called 'waste-spark' systems. A waste-spark system fires one coil for each pair of cylinders that are at top dead center (TDC) at the same time. These cylinder pairs are called 'running mates.' One cylinder is at TDC on the compression stroke, while the other is at TDC on the exhaust stroke. The spark in the cylinder at TDC on the compression stroke ignites the air-fuel mixture to produce power. The spark in the cylinder at TDC on the exhaust stroke is 'wasted,' hence the name 'waste-spark.' Each waste-spark DIS coil is hooked in series with its two spark plugs. As the coil fires, secondary current creates a high voltage spark across the gaps of both plugs. One plug fires with the traditional forward polarity of an ignition system: negative (—) to positive (+) The other plug fires with opposite polarity: positive (+) to negative (—) Thus, one plug always fires with what has always been called 'reversed polarity.' The voltage capacity of a DIS coil is high enough, however, to ensure that the available voltage is always high enough to fire the plug with reversed polarity when it's on the compression stroke.
Elements of the Secondary Ignition Pattern
These parameters are practically the same for all types of ignition systems.
It is very important to understand each part of the ignition coil waveform and what went into making the amplitude or voltage change over time. Without an in-depth understanding of the waveform, you will not know what has failed. For a proper diagnosis of this waveform you must pay close attention even to the smallest changes.
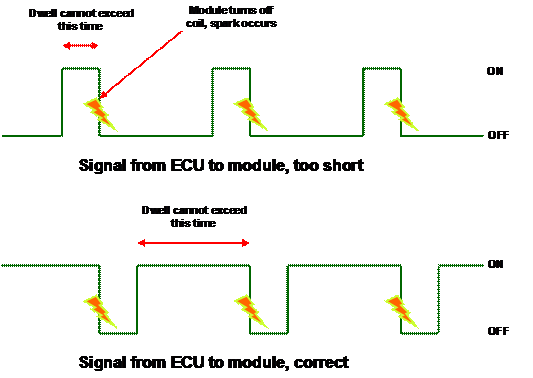
- Angle of closed state of contacts -(dwell angle or dwell period)
This is the angle on which the crankshaft rotates from the beginning of accumulation of energy in the primary winding of the ignition coil until occurring of the spark in the spark plug.
In ignition systems with mechanical switch, these are the degrees to which the crankshaft is rotated from the moment of closing the contacts of the breaker until they open again.
In ignition systems without mechanical switch, this is the time during which the ECU allows to current to flow through the primary winding of ignition coil. The beginning of the current flow is determined from the opening electronic powerful switch and in the end of the current flow and hence the appearance of the spark is determined by the time of obstruction of electronic powerful switch.
Dwell time is the length of time the coil primary circuit is being completed, and current is flowing through it. The initial oscillations in the pattern are the result of the initial build-up of the magnetic field that is created around any conductor with current passing. As that magnetic field builds in strength, it causes a 'Counter Electromotive Force' that opposes the current flow. This is why the pattern starts to take a slight upward slope.
- Advance angle
This is angle on which the crankshaft is rotating at the moment when the spark arises until reaching the relevant cylinder at the top dead center. One of main tasks of any ignition system is to ensure optimum angle of advance in case of a spark. To ensure maximum power, the mixture must be ignited before the piston, which is in pumping cycle to reach its top dead center - so after reaching the top dead gases can have a maximum pressure and maximum useful work carried out during the working stroke of the piston. Also any ignition system provides interrelationship between the angle of the advance of spark, engine speed and engine load. When a spark uprise at a time that does not correspond to the optimum advance angle deteriorates the engine performance and increases fuel consumption.
At higher speeds, the speed of movement of the pistons is increased at this time to burn the mixture does not change - so the spark must occur earlier. Therefore the advance must be increased.
At the same speed of the crankshaft, the throttle position (throttle) may vary. This means that the cylinder will form a mixture of different composition and burning rate of the mixture depends on its composition. At fully open throttle (fully depressed accelerator pedal) the mixture burns faster and should be lit later - thus, when the engine load is increased, you must reduce the advance. Conversely, when the throttle is not tightly closed, the burning rate of the working mixture is less, so you need to increase the advance.
- Drilling voltage - Firing Line
Dwell Lab Scope Coil Tester
This is the value of voltage in the secondary circuit at the time of appearance of the spark. In fact this is the maximum voltage in the secondary circuit. It directly depends on the distance between the electrodes of spark plugs and the mixture in the cylinders. A spark incurred at the time, which interrupts the current flow through the primary winding of the ignition coil. Typical value of this tension is between 7 kV and12 kV.
- Voltage combustion of the mixture - 'spark Kv'
The point when the actual spark across the gap starts to take place. This part of the pattern is called 'spark KV', or the energy required to actually initiate the spark and keep it going. Spark KV is affected by the actual resistance of the secondary circuit, from the ignition wire, through the plug, across the gap to ground. High spark Kv means higher than normal resistance, and lower spark Kv means lower than normal resistance. Tensions in the secondary circuit of ignition during the combustion of spark are usually between 1 kV-2 kV.
- Burn Time - spark line (also called 'spark duration')
Spark combustion length is normally between 1.5 mS to 2 mS.
The 'spark line' is the actual time the spark is moving across the plug gap. Normally, this should be between 1.5 mS to 2.0 mS. Anything under 0.8 mS usually means that a misfire has occurred. It is affected by the circuit resistance, just like spark KV,
but the neat thing about the burn line is that it is a window into the combustion process.
All these parameters are shown in fig.1 below.
Fig.1 Secondary ignition waveform
Procedure to verify the reliability of the secondary ignition circuit
— Ohmmeter and voltmeter measurements —
- Measure the coil's secondary winding resistance with ohmmeter. Normal resistance must be around 7000Ω.
- Switch ignition on but do not start the engine.
- Use a voltmeter to check whether battery voltage is applied to the coil's positive terminal (usually '2') and chassis ground.
— Oscilloscope measurements —
To perform a diagnosis of secondary voltage of all ignition systems, it is necessary to monitor the ignition coils secondary winding charge waveforms by clamping capacitive pick-up probes around each cylinder high tension lead.
To test all types of ignition systems, your oscilloscope must have features for motor tester (engine analyzer).
You can't use an ordinary lab scope!
If you are using an ordinary lab scope, you can still perform a secondary ignition measurement but you'll be observing only one cylinder waveform at a time. Then move the test probe to the next cylinder.
Distributor ignition system
- Connect a capacitive pick-up clamp to the coil wire, as close to the ignition coil as possible.
Connect the other capacitive pick-up clamp lead to the oscilloscope according to its instructions. - Connect a 1st cylinder trigger pick-up clamp to the spark plug wire №1, as close to the spark plug as possible.
Connect the other cylinder trigger pick-up clamp lead to the oscilloscope according to its instructions. - Start the engine and left idling.
- Watch the oscilloscope screen and compare it with the waveform in fig.2.
Normal operating parameters for an ignition system are as follows:
- Firing voltage - also known as break down voltage - on the average 4-18 kV;
- Spark voltage - also known as burn voltage 1-4 kV;
- Spark duration - also known as burn time 1-2 ms.
Note: The above values will change according to the air/fuel ratio and cylinder pressure.
Fig.2
DIS (Waste Spark)
To perform a diagnosis of secondary voltage of DIS ignition system, it is necessary to monitor the ignition coils secondary winding charge waveforms by inserting capacitive pickups to each cylinder HT cable.
If you are testing DIS – wasted spark and you have an access to the HT spark plugs leads, follow the specific instructions for your oscilloscope:
- Put a capacitive pick-up clamp on each cylinder and connect it according to the oscilloscope specific instructions.
- Start the engine and left it idling.
- Compare result with the waveform in fig.3.
Normal operating parameters for a DIS (Waste Spark) ignition system are as follows:
- firing voltage, also known as break down voltage – on the average 10…15 kV;
- spark voltage – also known as burn voltage 1…2 kV;
- spark duration – also known as burn time ~1,5 mS.
Fig.3
Direct Ignition (individual ignition)
If you are testing Direct Ignition (DI) system and you have an access to the HT spark plugs leads, follow the specific instructions for your oscilloscope.
The basic tested parameters at diagnostics of individual ignition are:
- presence of damped oscillations in the end of a site of burning of a spark between electrodes of a spark plug;
- duration of the period of accumulation of energy in a magnetic field of the individual ignition coil (usually 1,5…5,0 mS depending on the design of the coil);
- duration of burning of a spark between electrodes of a spark plug (usually 1,5…2,5 mS depending on the design of the coil). It is necessary to consider, that if the duration of spark burning between electrodes of a spark plug on any mode of engine work will be less than 0,5 mS because of the fail ignition coil, than the spark between electrodes of a spark plug will arise, but air/fuel mixture from such spark will not be ignited. If you are testing a COP system and you don't have an access to the HV cylinder spark plugs wires, there are two ways to test the secondary ignition system:
- with COP pick-up sensor
Fig.4 COP sensor
The COP sensor can be used as an additional pick-up probe to any automobile oscilloscope. The COP sensor is used to test the efficiency of a COP ignition system, it is used to determine whether the COP system makes the ignition sparks it's supposed to and their duration. The COP sensor transforms the signal induced in it by the ignition coil's high-voltage chain into a voltage pulse, which are shown on the oscilloscope's screen. These values are in direct relation to the voltaic arc produced by the spark plug. Because of the variety of ignition coils with different constructions, it should be noted that the COP sensor cannot determine the exact value of the voltage where the ignition spark appears, but it can be used for a comparative analysis between the different cylinders in order to determine which cylinder is not working properly.
With an ordinary lab scope you can use only one COP sensor to test each cylinder separately (one by one).
But if you want to test all cylinders simultaneously, you must use an engine analyzer (special oscilloscope with motor tester features). Also, the oscilloscope must have at least 4 channels.
Note: In this case you can't use an ordinary lab scope!
- Put a COP sensor on each cylinder and connect it according to the oscilloscope specific instructions.
Output voltage of the COP sensor is around 1-2 volts.
- Start the engine and left it idling.
- Compare result with the waveform in fig. 5.
Note: Secondary voltage can rise up to 40000V!
Fig.5
- with universal HT extension leads
Fig.6 Universal coil-on-plug extension lead
Universal coil-on-plug extension leads are designed to aid diagnostics on secondary ignition circuits by allowing an HT measurement to be made when there is no, or limited access, to any spark plug leads.
- Connect the universal coil-on-plug extension leads between the coil pack and the spark plugs for each cylinder.
- Than attach a capacitive secondary ignition pickup on each lead.
- Start the engine and left it idling.
- Compare result with the waveform in fig.5.
Note: Secondary voltage can rise up to 40000V!
— Typical reasons for malfunction of the secondary ignition circuit —
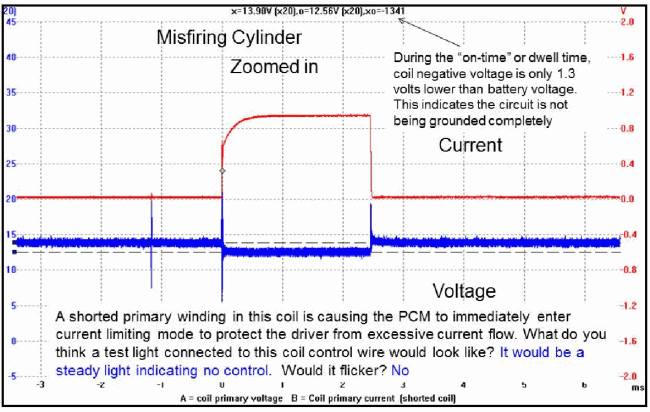
Windings of some compact individual ignition coils are executed so, that the secondary waveform of such coils little differs from the waveform shown above. The most essential difference is presence of damped oscillations after breakdown of a spark interval between electrodes of a spark plug.
Secondary waveform of the serviceable compact individual ignition coil,
received with help of the universal capacitive probe. Presence of damped oscillations after breakdown of a spark interval between electrodes of a spark plug (the site is noted by a symbol '2' in fig.6) is consequence of design features of the coil and not an attribute of malfunction.
Fig.6
Secondary waveform of the faulty compact individual ignition coil, received with help of the universal capacitive probe.
An attribute of malfunction is absence of damped oscillations after the ending of burning of a spark between electrodes of a spark plug (the site is noted by an arrow in fig.7).
Fig.7
• Bad HT lead(s).
• Bad isolation of the secondary coil (when COP system is present) - It is possible to find this malfunction by the the primary or the secondary waveform. Attribute of the breakdown between a coil isolation of the ignition coil is absence of damped oscillations in the finish of burning of the primary or the secondary waveform.
No spark? From 1989 to 2004 Suzuki Sidekicks, Trackers and Vitara's
See the no start page for a fast spark audit.
Index:
- G16A, SOHC valve spark. Early 1989/90
- G16B early (per 1996)
- G16B, SOHC 16v OBD2 (added CKP sensor ) 1996 and newer.
- All COP engines. V6 shown. also same for 2.0L I4's and the 1.8L I4:
- All 1.8L and up, CMP and CKP sensor facts. J18/20 1996 to 2004
- See my simple bench test video of one type of CMP hall sensors.(can be done on car, unplugged & cranking the engine.)
- See the CKP scope signals? and rules here? lots and lots of rules.
You tested for spark first here using the tried and true way.
USA centric, other counties the ignition can be different!
1989 to 1998 1.6L and up to 2005 on all 1.8L to 2.7L C.O.P coil based engine. Coil Over Plugs.
I try here, to cover all generations in the year range stated!.

The Ignition parts slide show.
This page attempts to cover 5 generations in 15 years span.
If spark is bad, all ECU's Cut Fuel injection!
Spare design evolution is complex, over 5 generations of radical changes.
Hints (top errors, to not make)
Do not do or forget:
To check all fuses!
Fail to check spark at each spark-plug and at the coil. (this combined information can save you lots of time)
Fail to discover the timing is way off and 100% proof the cam belt slipped. 'a timing light is only $20'
Read the Haynes books, the data on distributor rotations is wrong.
Forget you can check for spark with the timing light cranking, and see the cam has in fact slipped.
Pull the distributor, unless you learn how to re-time it from scratch.
Fail to see if the Cam is actually spinning! LOOK!
Fail to look for shorted spark plugs all 4 or 6 of them. for Fouled but they should look GOOD.
Fail to look at the factory dash tachometer, and see that it moves to 400 rpm (or tad less) cranking, No? then Igniter is dead.
Fail to make sure you didn't loose the Ignition suppressor module, no Tachometer cranking, and loss of injections as a result.
Fail to have ECU power, and grounds to ECU and distributor. per this ground check page.
Tools: a Timing light, if no timing light? your efforts are wasted, IMO!
Top fails /issues are:
- Fuses must all be good, there are 3 fuses for ECU and COIL.(see fuse maps here) IG-coil, Dome, 'FI'
- Timing belt slipped or snapped ( is cam spinning cranking? ) look down oil fill hole. See cam spin? no? If not, you have discovered your problem.
- Gross neglect of Distributor cap-rotor-wires-plugs ( called a tune up ).
- Top diagnostic error?, not checking Ignition timing for near TDC firing and missing the fact, that the cam timing belt has slipped!!!
- Rotor installed in the wrong position of 3, USA rotors can not be done this way, unless you buy fleabay China knockoff noname JUNK.
- Dead battery below 12.6vdc. ECU dies below 10v. (try to stay above 11v at all times, at the ECU)
- Not checking all 4 spark plugs for spark and if all 4 spark plugs are bad, checked directly at the coil. Possible on all years!
- Not checking the firing order of the spark wires ( 'THE HAYNES RAG', has this WRONG!) use mine.
- Not realizing the 8v and 16v Distributor rotors, spin in opposite directions.! (the Haynes shows this wrong.)
- Not doing the ECU LIVE DIAGNOSTIC CHECK below!
- Ignoring the DEAD CEL lamp and not checking the ECU for code 12, cranking. 12= OK.
- Not checking for DTC code 41 or 42 cranking for 10 seconds. or code P0340 on OBD2 cars (96+)
- Do not forget you can move the COP coils, to see if the misfire follows the COIL.
- Why are you working on any 1996+ or newer car with no full scan tool, huh? $78, and it is yours.
Check for spark all 5 places, (4 on Sports) each spark plug and at the COIL directly ( keep hands off ignition parts while cranking or get HIT hard)
You are certain that you have no spark at the COIL? now, but are you sure your Distributor rotor, is spinning?
In 1996+ the coil was moved inside the Distributor and is tad harder to test.
96+ So. use spare spark wires to test it. Use clip on the end. and new spark plug on the other, gapped to.028″
Do not gap this generation car, spark plugs over 0.028″ ever. Do not read gaps on spark plug boxes, ever!
Jargon used on this page.
CKP = crank position sensor. (antique name CPS, crank position sensor, I will not use the name CPS) The CKP on our cars is the VR coil type.
CMP = Cam position sensor HALL (on some cars it can be called CAS, cam angle sensor as found on 96+ 1.8L and larger engines.)
CAS = Cam Angle sensor (I will use this term only on 1.8L here)
VR = variable reluctance sender used with integrated igniter (89-90 only in USA and old Samurai)
Igniter, is a transistor module that turns on and charges the Induction COIL, and then releases it for the induced high voltage spark.
Suzuki moved the ignitor 6 times. But most Suzuk's the ignitor ended up inside the COP's.
COP = Coil over plug, one spark coil per spark plug.
Hall sensor, is a sensor that has coil and an amplifer all in one device, that is super reliable and needs no tuning (timing maybe up to 2001 or so) and has perfect 4v square waves outputted.
Coax= a shielded cable that allows the very tiny VR sensors signals to make it from the engine bay all the way to the ECU and still be viable signal, for sure cranking.
1989/90 Distributor issues:
First off, this Distributor (advance) works just like a 50,60,70s Chevy, it is 100% pure mechanical, the ECU does NOT MAKE SPARK! However the ECU does monitor (watch) the Tachometer line (brown wire for loss of primary spark signals and cuts fuel like they all do all years, when the brown wire goes dead.)
The ECU can not see, the loss of high voltage spark, not at all.
If you have an 1989/90 SideKick/Tracker.
89/90 :! No ECU needed for 89/90 Sidekicks to make spark! see end of page!
You can unplug the ECU and crank the engine over, and get spark all day. (but sure, no fueling happens)
It has a Vacuum advance, that can jam.
It has a mechanical advance, that can jam.(rust happens, just like in 1950, in the same exact ways) Same with its Vacuum Servo mech. advance.
It has a VR (variable reluctance) sender that needs to be gapped.
This is a pick up coil, or just a simple magnetic coil that senses a very weak signal and then sends that signal to the Igniter module, near by, #7. (you need a scope to see it.)
A high fail rate Igniter and VR sender. (likes to fail hot or random cut outs)
However 89/90 ECU does monitor spark! DTC 41. (diagnostic trouble codes)
The 89 has no DTC 42 codes, CMP started in 1991 and remains until today. (and in 1996 became P3xx DTC error codes)
Crank engine with Diagnostic jumper(fuse) in place for 5 seconds, see if code 41 throws.
If yes? Loss of spark, or a bad Suppressor module, bad coil, no power to coil, bad gap, bad VR, bad Distributor.
If you don't have a scope, you will be hard pressed to fix this Distributor.
Click to zoom 89/90 Distributor (slang for distributor) drawings, below.
Dwell Lab Scope Coil Placement
That crappy 89/90 distributor.
- Loves to die, due to VR bad, or the electronics module next to it or the Igniter next to them. VR gap must be.008 to.016 inches.
- Love to heat soak fail! (many newer cars with a CAS (cam sender up top) for same reason, heat soak on 1.8Liter and bigger motors)
- The Advance plate, can stick wide open, making person and motor quite crazy. Use the Strobe timing light to check static and advanced timing.
- The ECU monitors the spark and will show code 41, cranking, after 10 seconds of cranking ( diag jumper inserted) Don't fail to use this powerful tool
- Has Vacuum advance that can fail and diaphragm that can rupture and leak.
- This Kick motor will MAKE SPARK, with no ECU in the car (removed) The Distributor is Stand alone. (but you must keep spraying test fuel to keep motor going, with no ECU)
- Grab the top shaft there, inside the Distributor and wiggle it hard, does the VR gap change, yes? Well, time for a new rebuilt Distributor or new bearings.
- If I had this Distributor, I'd dismantle it and clean and lube the advance weights day 1, and put on a new fresh Vacuum advance. or buy the CARDONE. (link above)
- If spark keeps going bye-bye, at odd times, buy a new Distributor, or rebuild it totally but the CARDONE is cheaper that any DIY rebuild, the tiny parts are very expensive.
Main Induction SPARK Coil primary is 1.5 ohms, secondary about 12,000. spark wires,will measure 6.5k ohms per foot max. (OMG put in NGK blue mag wires, and don't mess about)
VR = variable reluctance sender.
Tools:
Harbor fright (pun) sells a Strobe light for a lousy $20, how can that be cheaper.? Mine cost me $400 in 2014 price adjusted dollars. back in 1980. (I have a modern, dial back tool too)
CHECKS! TO DO:
Cam not spinning? look down oil fill hole. Ignition timing way off (strobe light?), then the Timing belt stripped.
A snapped /stripped out timing belt.
This first section applies to 1.6L engines, see comments for 1.8L Sports that have COIL ON PLUG, 'COP'.
Wide gap tester only works on 1.8L and 99 and newer cars. Use a real spark plug on 1.6L (89-98)
Always use a fresh new spark plug to test for spark, any heat range is OK, but it must be never ran in an engine and must be gapped
to.028″ (AKA: '28 Thou',we call that), Never use post 99 large gap plugs or other 4J type plugs on 89-98 Kicks. It WILL MISFIRE.
I call this the rubber meets the road test, no fancy, hard to interpret, glow plug testers to confuse you.
Always check each spark plug wire tip for spark, then directly at the coil if any Plugs are dead/weak. 89 -95.?
96-98 1.6L has a hidden in 'Distributor' Induction coil and is tad harder to test it, so just check each of the 4 HV wires for spark.
96+ 1.6L ( all 4 spark plugs dead)
If you are patient, you could take a old spark wire/with spark plug boot, attach an alligator clip at the other end and attach this
clip to the coil top tower post, inside distributor, (cap and rotor removed) and test spark plug at the end.
Then cranking and looking for hot fat blue/white spark. Charged battery to 12.6v.
BTW: If the rotor is put on wrong or the dust cover ( it's not really a dust cover) is missing or cracked the spark will cross fire or misfire.
If you run this distributor set up in this way you risked destruction of the CMP, Igniter, or ECU. $$$$
This condition will be seen as spark missing on some spark wires. (new wires and sparks (tuned up)
Never allow the low voltage parts come into contact with the High Voltage parts. Do all you can do avoid that.
Clean it too. Clean the parts well all the insulating parts. Dirt conducts, at 50,000. Volts. Sure does.
Do not run the Distributor with the dust cover missing. Do not.
1.8L Sports / 2.0L and newer DOHC motors?,just pull the COP and insert a test spark plug, with the shell grounded to the valve cover.
COP is also called DIS, for Distributor LESS ignition systems found on 96 and newer 1.8L SPORTS and all 99 and newer USA cars.
TEST #1 ( never touch these parts when running or cranking, the voltage is very painful and risky your heart.)
The Spark tests ( best is to do each spark plug and coil if you can?)
Just pull #1 spark wire at the spark plug and connect a known good plug to the end of said wire, with the shell of the spark plug, touching the valve cover.
Have someone crank the engine and check for a fat blue/whit spark. (works on COP's too)
IF COP car (no, not police) repeat the above on all 4 spark plugs plug units.
If this first plug fails, immediately remove the test park and spark wire and move it directly to the Coil main High Voltage (HV) terminal.
Yes, remove Distributor cap center wire to COIL. ( On 96'+ with coil in 'Distributor' base) make up a test connection to the hidden coil.)
Pre 96 configuration:
Coil on firewall, HV spark cable to Dist. CAP and Distributor cap wires to each spark plug. HV= High Voltage.
Remove #1 spark wire from top of spark plug (twist the BOOT first, gently, then pull the boot, or you may wreck the wires)
Insert a new spark plug into the spark boot of this HV spark cable end. Any new spark plug will work 'J' plugs that can be gapped at 0.028″
On the early 89 to 95 Sidekicks only a few things must be good, to get spark.
Keep in mind 89/90 have an integrated Distributor with CMP and Igniter inside and has old fashioned, mechanical or vacuum advance inside.
Starting 91 the ECU now does all spark generation, the advance, and the Igniter was moved to the outside of the Distributor near the coil.
In 96 the igniter is moved back in to the inside of the 16v Distributor body. (USA rules) [ not 1.8L COP SPORTS]
Components are the same but there locations vary by year. ( the 89/90 as a magnetic VR (variable reluctance) device that generates spark directly)
Coil, Igniter, CMP (later called CAS), ECU. CAS/CMP is the CAM angle sensor in the base of the Distributor.
Starting in 91 the Cam turns, the CMP pulses, the ECU sees this pulse and generates a spark signal and sends this signal to the Igniter and then the Igniter powerfully pulses the induction coil and spark happens.
ECU LIVE DIAGNOSTIC TRICK!: 89-95′
The ECU has 2 secret test tricks to discover a bad CMP and or a bad Igniter. Special DTC 41 and 42 (91-95)
If you have no spark, you can install the DLC diagnostic jumper and crank the engine over for 5-10 seconds. DO NOT KEY OFF. crank for 10 seconds to be sure.
Release the key to ignition on position and look for CEL flashes.? DO NO KEY OFF! yet.
(if the CEL flashes are not 12,41,42, then pull the dome fuse for 1-2 minutes, put back and repeat this test) Dome fuse pull kills all ECU DTC memory storage.
The ECU looks at both the Ignition signal and the CMP signal, during this 3 second test. I do the test for 10 seconds to be sure. Never move.
If you receive any of the 2 codes below, then you have discovered the failure.
Code 12, OK, no fails.
Code 42 says the CMP signal is faulty. 91-95 P0340 fails on all 1996 and newer cars. (no diagnostic jump needed on 96+ but a scan tools is needed)
Code 41 says the Ignition failure.91-95 ( bad Coil or bad Igniter bad suppressor but on 89/90 bad distributor electronics.) (P030x, in 1996+ cars)
The ECU tries everything it can do, to make spark 91-98. Almost all sensors can be dead and the spark will happen (except the CMP).
You don't even need a starter motor or start position or ST signal to start the car, you can push start, the car and spark will happen, due to CMP spinning.
If CMP happens, the ECU generates spark during cranking.
On 89/90 years, the distributor is stand alone and makes its own spark (with external coil) the 80/90 needs no ECU to make any spark.
How ever, the 89/90 can report spark fail 41. Sims 4 cc ethnic hair.
Keep in mind, if the ECU throws a code, and the failure has been corrected, you need to clear the code by removing the DOME fuse above your left (USA) knee.
The Dome fuse is the memory power to the ECU.
Pulling this fuse, erases all DTC fails from memory. see fuse panels at the end of this page.
Pulling the battery will mess up radio (audio), alarm, and other fancy electronic options added to car the last 15 years. Don't do that.
Rarely does the COIL or Igniter fail on old 91-98 Kicks. very rare but on 1.8L the CAS loves to fail and fail hot. ( hot soak no starts, are classic this car 96-98)
If spark is good and DTC 41s throw (flash), the Ignition suppressor module is bad or loose or just fell off (not good the latter).
For COP type engines (1.8L). just move the coils around to see if the problem of now spark follows the suspected coil. Swap coils.
On all 96 and newer cars the ECU will log a pending or full DTC failure of P030x for bad spark or compression or bad injection. So called Misfire. 'A scan tool is a must'
89/90 the Distributor VR sensor and Igniter love to fail. ( no spark at all or flaky)
96-98 Sport 1.8L love to have bad CAS,CAM CMP sender. (and heat soak issues) Mark it before removing it.
CMP tests! (in the base of the 'Distributor', DTC code 42 fails) 1991-1998 (89/90 has no CMP, but has VR integrated Igniter)
DMM = Digital Multimeter. DSO = Digital Storage Oscilloscope or just Scope it.
Do not delay with tools, set your DMM to 20 volt range connect the minus lead to the metal of the engine. (or use DSO)
Connect the Red test lead of the DMM to the distributor white wire side connector (91-98,8v or 16v) (do not remove the connector,just back probe it)
Key on, and crank the motor, the DMM needle will swing from 0v to 5v and back to 0volts for each fining of each cylinder.
The CMP generates a nice 5vdc square wave as seen on a DSO, see photo of DSO below.
If you want to back probe the ECU these are the pins:
8 valve ECU pin A13 is the 16v CMP input pin.
16 Valve engine, this pin becomes the B3 pin.
If your car is a 1.6L 1996-98, the crank sensor will not kill spark but will throw codes if it does fail.
The CMP Acts just like a switch, open and closing. The ECU pulls the voltage to 5v (via ECU internal resistor ) and the CMP only switches this signal to ground.
There will be no spark or fuel injection, when the CMP goes dead for any reasons.
It must be grounded at the connector, it must have 12vdc at the connector.
Supporting documents.
Schematics
The loop library is adequate for creating simple tracks. 8 effects.Supported Audio File Formats:Import Export FLAC MIDI MP3 OGG Vorbis WAV WMA Note: Only non-copy-protected audio CDs can be imported. Studio beat maker free download. Supported Video File Formats:Import Export AVI MXV wmv.Overall, Music Maker is an easy suite to learn quickly for most users. The interface is easy to navigate and the sound production is crystal clear.
Click to zoom DSO photo below. (same wave form for 8v and 16v distributors, 91-98 only)
Below is actual 1991 8v G16 engine. This is input to ECU. If this dies (rare) spark ends.
We now cured the code DTC 42 failure, and if you still have spark failure, continue to the next frame below.
TESTING THE Igniter AND THE COIL SIDE, for spark loss.
The Igniter on all cars moved to many places in time, first the Distributor, then the Fire wall, then to the ECU internal. In all cases, it's just a power transistor.
Some engines have COPS, and the Igniter is inside each COP. (coil over plug)
Suzuki spells this as 'Igniter' I'll try to follow their lead.
Next I will show you how to test the Igniter / Coil and actually make and see spark.
Dwell Lab Scope Coil Mounts
First the 91-95′ 8v uses pin A12 as its Igniter driver pin at the ECU.
The 92-95′,16 V Igniter uses pin is A4 at the ECU.
The secret here, is that the Igniter input gate is a low impedance (resistance) pull down device and takes stronger currents to fire the Igniter.
I disconnect the ECU 'A' (white for 8v) connector and then, I then take my 150 ohm test resistor and connect 1 side to 12vdc (cigarette light plug will work) and
the other side of this resistor, I touch to the A4 or A12 (as appropriate to 8v/16v valve type) pin of the ECU harness connector.
If your car is a 1.6L 1996-98, the CMP pin is E34 Pin 4, orange. (integrated Distributor coil/cap, Igniter and CMP)
This act, turns on the Igniter and the coil starts charging up.
I touch this pin and release it, on each release there will be full power spark out the HV tower plug on the COIL.
When you jumper this resistor ( pull up resistor) to the Igniter gate the Igniter turns ON.
Do not charge the coil for more than 1 second in 30 seconds as to not over heat your coil.
The ignition must be turned on at the key, but no cranking.
I place a spark plug and spark plug directly to the coil for this test. (I put my test spark plug, where i can see it from cab, grounded shell,of course)
If this test fails, the Igniter or coil are bad. (check coil resistances per FSM spec) the coil primary is like 10 ohms and the secondary is like 20,000 ohms.
The below photo is of the actual ECU Igniter driver signal on the pin, 0 to 3.5v is the signal.
The Igniter is just a simple transistor that has a resistor to the input gate.
I need to use a 150 OHM, pull up resistor to achieve the 3 volt drive signal.
The pin marked gate is what the A4 or A12 pin on the ECU drives.
I avoid connecting 12vdc directly to the gate, as this might damage it. (it's expensive $ )
150 ohms has a color code of 'brown, Green, brown' = 1, 5, 1 1 and 5 and 1 zero.
The below is the actual Igniter that I reverse engineered (hacked).
The signal is from a scope on a running motor. (my simple graphic) the The transistor below IS the Igniter (91-95) 8V
Note the pull down resistor at the gate! the resistor keeps the transistor off, this pull down protects your coil from burning up. if you accidentally unplugged the ECU with the key on.
The coil can not survive infinite dwell (charging) on most cars.! For sure all these cars.
Drawing of Igniter mounted to Fire wall ignition coil.
The signal below is the Igniter module gate signal. 1991-98. (1991 actual, (I have 3 lab scopes)
The Igniter, is just a simple TRANSISTOR with a default pull down resistor, so it can not, by accident turn on and burn up a nice ignition coil. (the coil must never be on full time )
The Igniter charges the coil, then release it and INDUCTION happens (read Mr. Tesla's works)
, maximum.
My test resistor (166 ohms is max) I use a 150 ohm test resistor will flow 1/8 watt or more is ok.
A 1/8 watt 150 ohm resistor is all that is needed costing 3 cents (wholesale). Radio Shack has then for 50 cents.
One can use this 150 ohm resistor to test the Igniter on the car.!
If you have spark now, using the above test and the last frame (chapter) test for the CMP passed and you still don't have spark the ECU is bad.
If you have spark and you get code 41s, your suppressor is bad or missing. Engine my start and immediately die in the fail mode. and throw 41s.
Code 41's like All injections FAST, by ECU programming.
Photo 2:
The output of the Igniter below is on the top waveform, coil MINUS. see that kick, the Tachometer runs off that KICK.
The bottom wave form is the CAS/CMP signal. (bench testing ) 1991 8v.
Here is one more photo of the Coil primary (minus lug).
ODD things. or the rotor is indexed wrong. (China clone rotors do that, never BOSCH or SUZUKI Mitsubishi parts)
If someone timed the Distributor, so that the rotor is firing between cap posts, and not aligned PERFECTLY with #1 TDC, then spark at the plugs will be weak or dead.
If the coil checks out with a fat blue/white spark (never yellow or orange or weak looking) then the Ignition is working. The car battery must be fully charged to 12.6v.
Look for bad cap, rotor, wires, plugs or grossly bad timing of the distributor.
Careful don't get shocked, it hurts REAL BAD.
Test with hands in pockets, or be sorry. Electric shock is not only painful but dangerous, to your heart and can make you jump and get CUT REAL BAD!
Below are drawings of the most common Sidekick ignitions.
If all else fails to make spark, then the ECU is bad. but make sure all power pins on the ECU are at 12vdc, Key On. and all grounds are good.
8v only Power and Ground:
Drawing #1: 8v 91-95 only
OK Success you now have spark from the Ignition coil. So You do have spark, but maybe not at the spark plugs.
Now check spark at each plug.
if you do not have spark at the plugs, then there is only 2 possibilities.:
1: You need a new cap, rotor,wires and plugs ( this is called a tune up and these parts don't last long, 50k miles is a good rating on wires, cap and rotor)
2: The Distributor is mis-Timed grossly.
The below drawings demonstrates the minimum circuits needed to make spark, I may not show the fuses, but it does show battery. You do have power.
Always check spark under load, under the load of spark plug! or dangerous spark flash over can happen, shocking you or damaging the near by electronics parts.
My 8 valve Suzuki Side kick 1991-95, will spark all day long, with only these wires connected: This is called ECU Bench testing.
Drawing 2:
Next trick?
This is called ECU Bench testing.
if your car makes spark and then engine dies, after starting,then the spark filter suppressor is bad. (very rare). its just a 1000-2000 ohm resistor inside.
This device feeds back the spark signals to the ECU ( a monitor watches it) and if missing, kills injection of all fuel, or crash and fire safety.
16 Valve engine (92-95′): Drawing 3:
Note Spark plug connected directly to coil for a true spark test. If this test passes then reconnect distributor center lead and test each of the 4 cylinder plugs for spark.
The 92-98 SOHC 1.6L A new designed Distributor USA: G16 engine.
Note: Hidden COIL (induction)
One can do ECU Bench testing, if you create signals on the white wire the ECU will fire the Igniter transistor and the coil will charge and fire spark.
All you need is power to ECU (& ground) then your white wire pulses and you will see the Orange wire plus (O) called igniter drive.
With this simple diagram one can see how to do the testing, in the light of the above. (a scope at E33 White and E34 Orange will tell all you need)
All they did was move the Igniter to the inside of Distributor along with the COIL. ( the COIL is hidden in the bottle of the Distributor, not the cap)
Note the CMP sensor, does not drive the coil directly and only the ECU can make spark.
Keep in mind, each year 96-98 the ECU is vastly different [software wise ] (thanks to the EPA).
Note that the coil output can not be tested directly, easily, as the older cars could be done. but a test lead can be made up from an old spark wire.
An Alligator clip soldered to spark wire clip, then High voltage spark wire, to its spark boot then boot to tests spark plug. (3 parts) now you can test the coil output)
The Same OBD1, code 41 and code 42 tests work here too from 1992 to 1995 in USA.
Drawing 4:
On this ECU, I only need to make up a CMP HALL type (0-4v pulse) signal generator to pin 3 above. (white) and the bench tested ECU makes park (power wires with power to ECU sure)
The ECU cuts fuel if the brown wire goes dead. (spark read back pin) marked TACHO above. brown wire.
Photo 1: The 1996-98′ CKP sensor. CRANK sensor:
(oddly, it will not prevent starting, but will fail with a DTC code every time. and is used only to make spark more accurate! and for OBD2 misfire monitor, laws)
The EPA mandated this sensor, to the 1996 car and the 8valve TBI engine became illegal here (gone)
It is not a nice HALL sensor, it's just Va R coil sensor, with 2 wire.
Warning: there is no pan gasket, here, starting in 1996, only a RTV glued on pan, if you put a gasket here (as seen in 1995 kits), the CKP goes DEAD (or misfires {far worse that})
The Crank position sensor. USA 1996 and newer. ( the tone wheel is behind the cam cog on crank, it's now part of the cog in 1996)
Click to zoom 96 CKP sensor. Crank position sensor
As you can see the 96+ cars have a Crank Position Sensor CKP (SAE name). ( if it fails, you will get DTC codes for this sensor, and the results my be limphome.) You will fail smog with the CEL glowing for sure.
This device is for the more accurate timing, necessary for the NEW EPA mandated Misfire P030x monitors,of OBD2.
Car will start up, and run, with this device unplugged, but timing will be jittery. (timing belt jitter is real! as all 1995 did. 92-95)
The 96 car does use a CMP (inside the distributor) to make spark, but the CKP above, makes the spark dead accurate, they work together to make perfectly timed spark.
Keep in mind, a loose timing belt will make Misfire DTC's throw and may make this sensor, CKP may show up as bad, when NOT. (think about the cam bouncing madly and the CMP?)
On this OBD2 engine we crank the engine for 5 seconds. With the scan tool attached, and see RPM rise to 300 RPM(about) if not CKP is dead and look for DTC P0340 or P0355 or near.
If the CMP CAM sensor is shown as dead by the ECU scans, the engine will never start.
A dead CKP, the engine will will start, but many OBD2 features, will be inoperative. misfire detection will be dead. (P0300,301, to 304 will be logically DISABLED)
The below CKP is not a Suzuki but is same type and Quality, (ignore the #1 gap pulse below, we don't have that on the G16b) but the signal is 13 times weaker than the CMP at idle.
Cranking the signals will be far lower, (slow moving crank shaft and Faraday's laws win) Only a scope can see this signal, not some Test LED lamp or incandescent lamp, ever.
The signals can be as low as 200mV or 0.2v) while cranking slow in ALASKA. Photo 2: (the below is idling engine, if you speed it up, the signal gets stronger (taller))
On most cars made, if this signal is lost. there will not be spark ever. period. (but not THIS CAR)
Things that can cause CKP to be bad, and not the CKP being bad.
- Wires bad here, end to end. ECU to here (open, shorted, cut, crushed, smashed, rusty, corroded, or mangled)
- Damaged coax on these wires to it., OR no longer grounded at one end this shield, (only) The shield keeps noise off the line. (and needed big time cranking)
- Someone added a pan gasket (fail)
- The ECU is bad, (99.9% sure it's not) Inputs on most ECU never fail. (they are protected is why) but outputs love to fail.
- Someone put a 1992 to 1995 crank cog here, on this engine, with no tone wheel. (engine swaps?)
- Your scope is dead on this channel (LOL). Try channel 2. Test your scope leads, using the test port signal on the scope.
- Using the wrong sensor, or wrong year or off the WRONG CAR.
- If the ECU says its bad, it is. (CKP is bad or the wires, for sure the signal is too weak to read by the ECU)
- The accuracy of the reluctance sensor can also be affected by the sensor magnet attracting particles of ferrous material (from many sources, depends on the 3 common locations that, Front, center,rear of crank)
- If the Cam belt or chain is loose, many ECU will show gross errors with CKP or CMP or both, due to the gross slop of cam and jittering huge of the 2 sensors. (it compares the 2 and sees, omg, what is that bounce there?) BAM DTC errors.
- Watch here the 2000 year 5.7L Chevy 2500 fail to start. The CMP and CKP must align or it drops spark.
- Think about how dumb it would be for the ECU to fire one cylinder, way early,then fire the next way late (a tug of war). (the to pistons rods are going to be stressed hard) question?, why should it? (easy answer) (cuts spark it can)
- To this, add CAM TIMING WAY OFF. (or out of control)
Seems cleaning it first, makes sense, that is, if that act does not destroy the calibration of said sensor, so read the FSM and learn that first, then clean it. (factory serv. manual)
My JEEP must be calibrated, as just one example. (shimmed out) (we use a tape shim) at the flywheel bell mount.
End G16 engine.
1996-1998 1.8Liter DOHC Suzuki Sports. How spark happens? (creation) (and 2.0L and newer and bigger engines.)
OBD2 only USA, cars.See a slide show:
REVIEW:
The new Engines have 2 sensors, to make spark.
The CMP is really 2 sensors in one. It is a high power, 5vdc driver on 2 pins.
The CKP is just crankshaft coil for #1 TDC precision crank positions. (this is a TDC strobe, and is weak 1v signal).
The Engine may run with a dead CKP, like the G16 does, I do not know. But for sure P0300 will happen. and P0335s
When the CMP dies or goes to sleep hot, or misfires, you will get P0340 errors, (DTC)
The FSM clearly states to crank for 10 seconds or run engine for 10 seconds to set these, DTC live or pending errors.
Do not look at the stupid CEL lamp, it's mostly useless, use a real scan too, and do live testing.
These 2 sensors, set the drum beat for the ECU, and it then decides, when and how to make spark, the PCM decides all spark advance, by using tables and live data.
The PCM then fires the COP coils in the firing order 1,3,4,2 (2.0L)
If fuses are good and the COPS are dead, then you need to use a scan tool. You can NOT FIX cars with any CAN TOOL, so buy one for $9 and WIN.
The CKP crank sensor, never fails and is behind the engine, behind the flywheel or A/T flex plate. as seen here. and here.
The CKP and CMP work together, so the ECU can detect P030x misfiring. ( this began in 1996 for all USA OBD2 ECU's)
When any cylinder fires, the combustion causes a very fast acceleration of the crank shaft, all 3 sensors are used to measure this rate of acceleration.
The OBD2 misfire monitor can in fact tell you, which cylinder misfires.
Three thing happen here, injector timing, spark and OBD2 misfire monitoring.
The Fly wheel has holes cut, to make the CKP function. (see slide show above) My V6 2.5L has the same parts. (nearly) only more holes cut in the flex/fly plate.
The ECU will throw codes for failure of either the CKP or the CMP. Or throw DTC P0300 {misfire} or P030n (where n = cylinder failing 1-4)
DO NOT FAIL TO LOOK carefully at the OBD2 scan tools pending DTC fail tables.!!! LOOK.
If the engine does not start?, SCAN it for 5 seconds cranking, IT WILL throw a code, LOOK for it. NOT 1 second, 5!
Scan, crank and look for 5 seconds!!!
If the engine cams, have a loose timing chain, it will throw random misfire codes.
This CMP device likes to fail during HOT restarts (called heat soak fails).
DO NOT remove the CMP at cam rear, with out putting index marks on the base mounts, with a center punch or with scribe markers. 'called match marking'
(on newer, cars 2004 for sure, you need a special scan tool to set ignition timing doing a FREEZE (FIX timing command), Do not mess with the CMP until you have plan!
DO NOT PULL the CMP off the head, on newer cars that have NO TIMING FREEZE JUMPER! (1996 to 2003) Suzuki does have the jumper.
But you CAN, if you mark it very carefully! (scribe it) and win.
IF you can not find DLC2, better have a plan. (like how to time a new sensor).?
The real Suzuki's 1996 to 2004 I think all have a DLC2 connector (at right headlight rear shell or at left strut towner in the engine bay) 6 pins, jumper D to E or 4 to 5, to freeze timing.
The 2000 to 2004 Chevy trackers have no DLC2, and need factory scan tool to set spark timing.
For sure my 2004 DLC2 is missing, (and pray every day, the CMP never fails, now that Suzuki is Chapter 11.)
I got mine scribed, now.
THE CAM SENSOR:
This is the timing spec page. CMP.
CMP signals, both sides (pins) to ground. FSM. 2004
NO Scope CMP tests?:
One can check both outputs of the CMP with any simple analog voltmeter. (per 2004 Vitara 2.0Ll FSM)
Both pins have powerful driver transistors, making the test, easy.
Key on: engine off (emg. brake set, in park or neutral, and wheels chocked)
Nothing disconnected.
Back probing the 4 CMP pins (use a leather sewing needle, to back probe this CMP connector)
Both Pins on the CMP pins 4 is REF and pin 5 is POS, signals, toggle per below: (meter ground lead to engine block metal ground.
Ref. pin 4 toggles 0 to 5v, key on, turning crank slowly by hand, 6 pulses (needle wags) per turn of crank pulley, and see it pulse. (color Y/B)
POS pin 3, toggles just the same, but 360 times per crank turn. easy huh, just a $10 walfart meter and I saved you 200 bucks. (color Y/G)
Pin 2 is 12vdc key on (color BL/B). This the power pin. If 0v the CMP will be dead with no power. (cut wire?)
Pin 1 is 0v key on. it is ECU ground. (color Gr/Y) (0 to 0.5v) of above this the wire is cut or PCM is unplugged.
WATCH OUT, IT LOVES TO FAIL HOT. Sadly as you set up to the these tests, the CMP cools and it starts working. (buy a new one or rebuilt from Cardone for $150)
THE CRANK SENSOR IS NEXT:
Key off, unplug CKP. (rear of block, connector)
The CKP crank sensor is just a 550 ohm mag coil (+/- 100 ohms on CKP pin 1 and 2. (unplugged,) this is just a coil, and has no transistor drivers, like the above, so in this case, only a scope works for a true test. But do use the Ohm meter (resistance) to check pin 1 to 2. (2k ohm meter scale/ range)
If it reads infinity the sensor is bad. (very very rare, this) and takes removing the transmission to replace it.
DTC errors. P0335, if you don't get that DTC, I'd never replace it.
C.O.P'S: 'Coils Over Plugs' or D.I.S (Distributor less Ignition Systems)
No, not the Police! not coppers. 1.8L, 2.0L and bigger,
The 1996 to 2004 USA.
We can have 4 Coils or 6 on a V6 or less (European have wasted spark coil packs (2 in 1 brick).)
COP Ignition COILS. HOW TO TEST COP SPARK IS HERE?
Our V6 has 6 COPS. The USA 1.8L and 2.0L have 4 COP's
Some odd 2 COP wasted spark cars (non USA), are wired is series (HV side), 2 spark plugs fire at once, one on compression and one on exhaust stroke (wasted)
(wasted spark is used on some Kicks, outside of the USA) My 71 Honda CB750 had this long ago, its not a new idea.
(this new system can run.044 ' spark gaps 1999+ only, it is way more powerful that the old generation 96-98 USA Cops that run.028″ gaps)
Again the same tests apply to this engine as the G16B 1996 and newer engines and that is…
On this OBD2 engine we crank the engine for 5 seconds. With the scan tool attached, and see RPM rise to 300 RPM(about) if not CKP is dead and look for DTC P0340 or P0355 or near.
If the CMP sensor is shown as dead by the ECU the engine will never start. A dead CKP, the engine will will start but many OBD2 features, will be inop. misfire detection will be dead.
Dwell Lab Scope Coil Kit
The 1.8Liter Sport: Uses Coil Over Plugs, called a COP.
Aka: Distributor -less – Ignition Systems or DIS.
If you have a dead COP, best way to test it is swap it with on of the other COPS and do a new spark test at each and every COP.
Just lay COP and plug on valve cover and crank and observe.( use a fresh new spark plug to accurate testing)
The 96 -97 COP is different from the 1998 then early COPS had a firewall mounted Igniter transistor block that can fail. (rare for sure)
The 98 COP has the Igniter moved to the inside of the COP coil. do not try to mix COPS from 96/7 to 98 vehicles or you will burn up the ECU.!!
Do NOT.
The Igniters are very reliable. See my tune up page for better photos.
These newest cops fit all Esteems and the 98 fits the 2.0L motor and my 2.5L. the p/n is -77Enn, make sure the nn matches. 98 and newer P/N: 33410-77E21 (cop)
Like regular spark coils the early COPS can be tested just like there former selfs.
a very low resistance primary 0.61-0.73 ohms /
and very high secondary resistance, 2k (2000) to 30k or 30,000 ohms or more. all readings of all coils very by year.! on most Ignition coils but on cops they are way higher.
The COP Igniter transistors were moved into the COP in 1998, deleting the fire wall mounted 4 way Igniter.

96-97 Sport Cops look like this: note the lack of transistors in COP, which means they can be bench tested very easy. (but must be pulsed or they will burn up)
98+ year Cops, see schematic have integrated Igniters, see Schematic here. note the transistors are off, and makes testing primaries very hard.
The Ignition parts slide show.
This page attempts to cover 5 generations in 15 years span.
If spark is bad, all ECU's Cut Fuel injection!
Spare design evolution is complex, over 5 generations of radical changes.
Hints (top errors, to not make)
Do not do or forget:
To check all fuses!
Fail to check spark at each spark-plug and at the coil. (this combined information can save you lots of time)
Fail to discover the timing is way off and 100% proof the cam belt slipped. 'a timing light is only $20'
Read the Haynes books, the data on distributor rotations is wrong.
Forget you can check for spark with the timing light cranking, and see the cam has in fact slipped.
Pull the distributor, unless you learn how to re-time it from scratch.
Fail to see if the Cam is actually spinning! LOOK!
Fail to look for shorted spark plugs all 4 or 6 of them. for Fouled but they should look GOOD.
Fail to look at the factory dash tachometer, and see that it moves to 400 rpm (or tad less) cranking, No? then Igniter is dead.
Fail to make sure you didn't loose the Ignition suppressor module, no Tachometer cranking, and loss of injections as a result.
Fail to have ECU power, and grounds to ECU and distributor. per this ground check page.
Tools: a Timing light, if no timing light? your efforts are wasted, IMO!
Top fails /issues are:
- Fuses must all be good, there are 3 fuses for ECU and COIL.(see fuse maps here) IG-coil, Dome, 'FI'
- Timing belt slipped or snapped ( is cam spinning cranking? ) look down oil fill hole. See cam spin? no? If not, you have discovered your problem.
- Gross neglect of Distributor cap-rotor-wires-plugs ( called a tune up ).
- Top diagnostic error?, not checking Ignition timing for near TDC firing and missing the fact, that the cam timing belt has slipped!!!
- Rotor installed in the wrong position of 3, USA rotors can not be done this way, unless you buy fleabay China knockoff noname JUNK.
- Dead battery below 12.6vdc. ECU dies below 10v. (try to stay above 11v at all times, at the ECU)
- Not checking all 4 spark plugs for spark and if all 4 spark plugs are bad, checked directly at the coil. Possible on all years!
- Not checking the firing order of the spark wires ( 'THE HAYNES RAG', has this WRONG!) use mine.
- Not realizing the 8v and 16v Distributor rotors, spin in opposite directions.! (the Haynes shows this wrong.)
- Not doing the ECU LIVE DIAGNOSTIC CHECK below!
- Ignoring the DEAD CEL lamp and not checking the ECU for code 12, cranking. 12= OK.
- Not checking for DTC code 41 or 42 cranking for 10 seconds. or code P0340 on OBD2 cars (96+)
- Do not forget you can move the COP coils, to see if the misfire follows the COIL.
- Why are you working on any 1996+ or newer car with no full scan tool, huh? $78, and it is yours.
Check for spark all 5 places, (4 on Sports) each spark plug and at the COIL directly ( keep hands off ignition parts while cranking or get HIT hard)
You are certain that you have no spark at the COIL? now, but are you sure your Distributor rotor, is spinning?
In 1996+ the coil was moved inside the Distributor and is tad harder to test.
96+ So. use spare spark wires to test it. Use clip on the end. and new spark plug on the other, gapped to.028″
Do not gap this generation car, spark plugs over 0.028″ ever. Do not read gaps on spark plug boxes, ever!
Jargon used on this page.
CKP = crank position sensor. (antique name CPS, crank position sensor, I will not use the name CPS) The CKP on our cars is the VR coil type.
CMP = Cam position sensor HALL (on some cars it can be called CAS, cam angle sensor as found on 96+ 1.8L and larger engines.)
CAS = Cam Angle sensor (I will use this term only on 1.8L here)
VR = variable reluctance sender used with integrated igniter (89-90 only in USA and old Samurai)
Igniter, is a transistor module that turns on and charges the Induction COIL, and then releases it for the induced high voltage spark.
Suzuki moved the ignitor 6 times. But most Suzuk's the ignitor ended up inside the COP's.
COP = Coil over plug, one spark coil per spark plug.
Hall sensor, is a sensor that has coil and an amplifer all in one device, that is super reliable and needs no tuning (timing maybe up to 2001 or so) and has perfect 4v square waves outputted.
Coax= a shielded cable that allows the very tiny VR sensors signals to make it from the engine bay all the way to the ECU and still be viable signal, for sure cranking.
1989/90 Distributor issues:
First off, this Distributor (advance) works just like a 50,60,70s Chevy, it is 100% pure mechanical, the ECU does NOT MAKE SPARK! However the ECU does monitor (watch) the Tachometer line (brown wire for loss of primary spark signals and cuts fuel like they all do all years, when the brown wire goes dead.)
The ECU can not see, the loss of high voltage spark, not at all.
If you have an 1989/90 SideKick/Tracker.
89/90 :! No ECU needed for 89/90 Sidekicks to make spark! see end of page!
You can unplug the ECU and crank the engine over, and get spark all day. (but sure, no fueling happens)
It has a Vacuum advance, that can jam.
It has a mechanical advance, that can jam.(rust happens, just like in 1950, in the same exact ways) Same with its Vacuum Servo mech. advance.
It has a VR (variable reluctance) sender that needs to be gapped.
This is a pick up coil, or just a simple magnetic coil that senses a very weak signal and then sends that signal to the Igniter module, near by, #7. (you need a scope to see it.)
A high fail rate Igniter and VR sender. (likes to fail hot or random cut outs)
However 89/90 ECU does monitor spark! DTC 41. (diagnostic trouble codes)
The 89 has no DTC 42 codes, CMP started in 1991 and remains until today. (and in 1996 became P3xx DTC error codes)
Crank engine with Diagnostic jumper(fuse) in place for 5 seconds, see if code 41 throws.
If yes? Loss of spark, or a bad Suppressor module, bad coil, no power to coil, bad gap, bad VR, bad Distributor.
If you don't have a scope, you will be hard pressed to fix this Distributor.
Click to zoom 89/90 Distributor (slang for distributor) drawings, below.
Dwell Lab Scope Coil Placement
That crappy 89/90 distributor.
- Loves to die, due to VR bad, or the electronics module next to it or the Igniter next to them. VR gap must be.008 to.016 inches.
- Love to heat soak fail! (many newer cars with a CAS (cam sender up top) for same reason, heat soak on 1.8Liter and bigger motors)
- The Advance plate, can stick wide open, making person and motor quite crazy. Use the Strobe timing light to check static and advanced timing.
- The ECU monitors the spark and will show code 41, cranking, after 10 seconds of cranking ( diag jumper inserted) Don't fail to use this powerful tool
- Has Vacuum advance that can fail and diaphragm that can rupture and leak.
- This Kick motor will MAKE SPARK, with no ECU in the car (removed) The Distributor is Stand alone. (but you must keep spraying test fuel to keep motor going, with no ECU)
- Grab the top shaft there, inside the Distributor and wiggle it hard, does the VR gap change, yes? Well, time for a new rebuilt Distributor or new bearings.
- If I had this Distributor, I'd dismantle it and clean and lube the advance weights day 1, and put on a new fresh Vacuum advance. or buy the CARDONE. (link above)
- If spark keeps going bye-bye, at odd times, buy a new Distributor, or rebuild it totally but the CARDONE is cheaper that any DIY rebuild, the tiny parts are very expensive.
Main Induction SPARK Coil primary is 1.5 ohms, secondary about 12,000. spark wires,will measure 6.5k ohms per foot max. (OMG put in NGK blue mag wires, and don't mess about)
VR = variable reluctance sender.
Tools:
Harbor fright (pun) sells a Strobe light for a lousy $20, how can that be cheaper.? Mine cost me $400 in 2014 price adjusted dollars. back in 1980. (I have a modern, dial back tool too)
CHECKS! TO DO:
Cam not spinning? look down oil fill hole. Ignition timing way off (strobe light?), then the Timing belt stripped.
A snapped /stripped out timing belt.
This first section applies to 1.6L engines, see comments for 1.8L Sports that have COIL ON PLUG, 'COP'.
Wide gap tester only works on 1.8L and 99 and newer cars. Use a real spark plug on 1.6L (89-98)
Always use a fresh new spark plug to test for spark, any heat range is OK, but it must be never ran in an engine and must be gapped
to.028″ (AKA: '28 Thou',we call that), Never use post 99 large gap plugs or other 4J type plugs on 89-98 Kicks. It WILL MISFIRE.
I call this the rubber meets the road test, no fancy, hard to interpret, glow plug testers to confuse you.
Always check each spark plug wire tip for spark, then directly at the coil if any Plugs are dead/weak. 89 -95.?
96-98 1.6L has a hidden in 'Distributor' Induction coil and is tad harder to test it, so just check each of the 4 HV wires for spark.
96+ 1.6L ( all 4 spark plugs dead)
If you are patient, you could take a old spark wire/with spark plug boot, attach an alligator clip at the other end and attach this
clip to the coil top tower post, inside distributor, (cap and rotor removed) and test spark plug at the end.
Then cranking and looking for hot fat blue/white spark. Charged battery to 12.6v.
BTW: If the rotor is put on wrong or the dust cover ( it's not really a dust cover) is missing or cracked the spark will cross fire or misfire.
If you run this distributor set up in this way you risked destruction of the CMP, Igniter, or ECU. $$$$
This condition will be seen as spark missing on some spark wires. (new wires and sparks (tuned up)
Never allow the low voltage parts come into contact with the High Voltage parts. Do all you can do avoid that.
Clean it too. Clean the parts well all the insulating parts. Dirt conducts, at 50,000. Volts. Sure does.
Do not run the Distributor with the dust cover missing. Do not.
1.8L Sports / 2.0L and newer DOHC motors?,just pull the COP and insert a test spark plug, with the shell grounded to the valve cover.
COP is also called DIS, for Distributor LESS ignition systems found on 96 and newer 1.8L SPORTS and all 99 and newer USA cars.
TEST #1 ( never touch these parts when running or cranking, the voltage is very painful and risky your heart.)
The Spark tests ( best is to do each spark plug and coil if you can?)
Just pull #1 spark wire at the spark plug and connect a known good plug to the end of said wire, with the shell of the spark plug, touching the valve cover.
Have someone crank the engine and check for a fat blue/whit spark. (works on COP's too)
IF COP car (no, not police) repeat the above on all 4 spark plugs plug units.
If this first plug fails, immediately remove the test park and spark wire and move it directly to the Coil main High Voltage (HV) terminal.
Yes, remove Distributor cap center wire to COIL. ( On 96'+ with coil in 'Distributor' base) make up a test connection to the hidden coil.)
Pre 96 configuration:
Coil on firewall, HV spark cable to Dist. CAP and Distributor cap wires to each spark plug. HV= High Voltage.
Remove #1 spark wire from top of spark plug (twist the BOOT first, gently, then pull the boot, or you may wreck the wires)
Insert a new spark plug into the spark boot of this HV spark cable end. Any new spark plug will work 'J' plugs that can be gapped at 0.028″
On the early 89 to 95 Sidekicks only a few things must be good, to get spark.
Keep in mind 89/90 have an integrated Distributor with CMP and Igniter inside and has old fashioned, mechanical or vacuum advance inside.
Starting 91 the ECU now does all spark generation, the advance, and the Igniter was moved to the outside of the Distributor near the coil.
In 96 the igniter is moved back in to the inside of the 16v Distributor body. (USA rules) [ not 1.8L COP SPORTS]
Components are the same but there locations vary by year. ( the 89/90 as a magnetic VR (variable reluctance) device that generates spark directly)
Coil, Igniter, CMP (later called CAS), ECU. CAS/CMP is the CAM angle sensor in the base of the Distributor.
Starting in 91 the Cam turns, the CMP pulses, the ECU sees this pulse and generates a spark signal and sends this signal to the Igniter and then the Igniter powerfully pulses the induction coil and spark happens.
ECU LIVE DIAGNOSTIC TRICK!: 89-95′
The ECU has 2 secret test tricks to discover a bad CMP and or a bad Igniter. Special DTC 41 and 42 (91-95)
If you have no spark, you can install the DLC diagnostic jumper and crank the engine over for 5-10 seconds. DO NOT KEY OFF. crank for 10 seconds to be sure.
Release the key to ignition on position and look for CEL flashes.? DO NO KEY OFF! yet.
(if the CEL flashes are not 12,41,42, then pull the dome fuse for 1-2 minutes, put back and repeat this test) Dome fuse pull kills all ECU DTC memory storage.
The ECU looks at both the Ignition signal and the CMP signal, during this 3 second test. I do the test for 10 seconds to be sure. Never move.
If you receive any of the 2 codes below, then you have discovered the failure.
Code 12, OK, no fails.
Code 42 says the CMP signal is faulty. 91-95 P0340 fails on all 1996 and newer cars. (no diagnostic jump needed on 96+ but a scan tools is needed)
Code 41 says the Ignition failure.91-95 ( bad Coil or bad Igniter bad suppressor but on 89/90 bad distributor electronics.) (P030x, in 1996+ cars)
The ECU tries everything it can do, to make spark 91-98. Almost all sensors can be dead and the spark will happen (except the CMP).
You don't even need a starter motor or start position or ST signal to start the car, you can push start, the car and spark will happen, due to CMP spinning.
If CMP happens, the ECU generates spark during cranking.
On 89/90 years, the distributor is stand alone and makes its own spark (with external coil) the 80/90 needs no ECU to make any spark.
How ever, the 89/90 can report spark fail 41. Sims 4 cc ethnic hair.
Keep in mind, if the ECU throws a code, and the failure has been corrected, you need to clear the code by removing the DOME fuse above your left (USA) knee.
The Dome fuse is the memory power to the ECU.
Pulling this fuse, erases all DTC fails from memory. see fuse panels at the end of this page.
Pulling the battery will mess up radio (audio), alarm, and other fancy electronic options added to car the last 15 years. Don't do that.
Rarely does the COIL or Igniter fail on old 91-98 Kicks. very rare but on 1.8L the CAS loves to fail and fail hot. ( hot soak no starts, are classic this car 96-98)
If spark is good and DTC 41s throw (flash), the Ignition suppressor module is bad or loose or just fell off (not good the latter).
For COP type engines (1.8L). just move the coils around to see if the problem of now spark follows the suspected coil. Swap coils.
On all 96 and newer cars the ECU will log a pending or full DTC failure of P030x for bad spark or compression or bad injection. So called Misfire. 'A scan tool is a must'
89/90 the Distributor VR sensor and Igniter love to fail. ( no spark at all or flaky)
96-98 Sport 1.8L love to have bad CAS,CAM CMP sender. (and heat soak issues) Mark it before removing it.
CMP tests! (in the base of the 'Distributor', DTC code 42 fails) 1991-1998 (89/90 has no CMP, but has VR integrated Igniter)
DMM = Digital Multimeter. DSO = Digital Storage Oscilloscope or just Scope it.
Do not delay with tools, set your DMM to 20 volt range connect the minus lead to the metal of the engine. (or use DSO)
Connect the Red test lead of the DMM to the distributor white wire side connector (91-98,8v or 16v) (do not remove the connector,just back probe it)
Key on, and crank the motor, the DMM needle will swing from 0v to 5v and back to 0volts for each fining of each cylinder.
The CMP generates a nice 5vdc square wave as seen on a DSO, see photo of DSO below.
If you want to back probe the ECU these are the pins:
8 valve ECU pin A13 is the 16v CMP input pin.
16 Valve engine, this pin becomes the B3 pin.
If your car is a 1.6L 1996-98, the crank sensor will not kill spark but will throw codes if it does fail.
The CMP Acts just like a switch, open and closing. The ECU pulls the voltage to 5v (via ECU internal resistor ) and the CMP only switches this signal to ground.
There will be no spark or fuel injection, when the CMP goes dead for any reasons.
It must be grounded at the connector, it must have 12vdc at the connector.
Supporting documents.
Schematics
The loop library is adequate for creating simple tracks. 8 effects.Supported Audio File Formats:Import Export FLAC MIDI MP3 OGG Vorbis WAV WMA Note: Only non-copy-protected audio CDs can be imported. Studio beat maker free download. Supported Video File Formats:Import Export AVI MXV wmv.Overall, Music Maker is an easy suite to learn quickly for most users. The interface is easy to navigate and the sound production is crystal clear.
Click to zoom DSO photo below. (same wave form for 8v and 16v distributors, 91-98 only)
Below is actual 1991 8v G16 engine. This is input to ECU. If this dies (rare) spark ends.
We now cured the code DTC 42 failure, and if you still have spark failure, continue to the next frame below.
TESTING THE Igniter AND THE COIL SIDE, for spark loss.
The Igniter on all cars moved to many places in time, first the Distributor, then the Fire wall, then to the ECU internal. In all cases, it's just a power transistor.
Some engines have COPS, and the Igniter is inside each COP. (coil over plug)
Suzuki spells this as 'Igniter' I'll try to follow their lead.
Next I will show you how to test the Igniter / Coil and actually make and see spark.
Dwell Lab Scope Coil Mounts
First the 91-95′ 8v uses pin A12 as its Igniter driver pin at the ECU.
The 92-95′,16 V Igniter uses pin is A4 at the ECU.
The secret here, is that the Igniter input gate is a low impedance (resistance) pull down device and takes stronger currents to fire the Igniter.
I disconnect the ECU 'A' (white for 8v) connector and then, I then take my 150 ohm test resistor and connect 1 side to 12vdc (cigarette light plug will work) and
the other side of this resistor, I touch to the A4 or A12 (as appropriate to 8v/16v valve type) pin of the ECU harness connector.
If your car is a 1.6L 1996-98, the CMP pin is E34 Pin 4, orange. (integrated Distributor coil/cap, Igniter and CMP)
This act, turns on the Igniter and the coil starts charging up.
I touch this pin and release it, on each release there will be full power spark out the HV tower plug on the COIL.
When you jumper this resistor ( pull up resistor) to the Igniter gate the Igniter turns ON.
Do not charge the coil for more than 1 second in 30 seconds as to not over heat your coil.
The ignition must be turned on at the key, but no cranking.
I place a spark plug and spark plug directly to the coil for this test. (I put my test spark plug, where i can see it from cab, grounded shell,of course)
If this test fails, the Igniter or coil are bad. (check coil resistances per FSM spec) the coil primary is like 10 ohms and the secondary is like 20,000 ohms.
The below photo is of the actual ECU Igniter driver signal on the pin, 0 to 3.5v is the signal.
The Igniter is just a simple transistor that has a resistor to the input gate.
I need to use a 150 OHM, pull up resistor to achieve the 3 volt drive signal.
The pin marked gate is what the A4 or A12 pin on the ECU drives.
I avoid connecting 12vdc directly to the gate, as this might damage it. (it's expensive $ )
150 ohms has a color code of 'brown, Green, brown' = 1, 5, 1 1 and 5 and 1 zero.
The below is the actual Igniter that I reverse engineered (hacked).
The signal is from a scope on a running motor. (my simple graphic) the The transistor below IS the Igniter (91-95) 8V
Note the pull down resistor at the gate! the resistor keeps the transistor off, this pull down protects your coil from burning up. if you accidentally unplugged the ECU with the key on.
The coil can not survive infinite dwell (charging) on most cars.! For sure all these cars.
Drawing of Igniter mounted to Fire wall ignition coil.
The signal below is the Igniter module gate signal. 1991-98. (1991 actual, (I have 3 lab scopes)
The Igniter, is just a simple TRANSISTOR with a default pull down resistor, so it can not, by accident turn on and burn up a nice ignition coil. (the coil must never be on full time )
The Igniter charges the coil, then release it and INDUCTION happens (read Mr. Tesla's works)
, maximum.
My test resistor (166 ohms is max) I use a 150 ohm test resistor will flow 1/8 watt or more is ok.
A 1/8 watt 150 ohm resistor is all that is needed costing 3 cents (wholesale). Radio Shack has then for 50 cents.
One can use this 150 ohm resistor to test the Igniter on the car.!
If you have spark now, using the above test and the last frame (chapter) test for the CMP passed and you still don't have spark the ECU is bad.
If you have spark and you get code 41s, your suppressor is bad or missing. Engine my start and immediately die in the fail mode. and throw 41s.
Code 41's like All injections FAST, by ECU programming.
Photo 2:
The output of the Igniter below is on the top waveform, coil MINUS. see that kick, the Tachometer runs off that KICK.
The bottom wave form is the CAS/CMP signal. (bench testing ) 1991 8v.
Here is one more photo of the Coil primary (minus lug).
ODD things. or the rotor is indexed wrong. (China clone rotors do that, never BOSCH or SUZUKI Mitsubishi parts)
If someone timed the Distributor, so that the rotor is firing between cap posts, and not aligned PERFECTLY with #1 TDC, then spark at the plugs will be weak or dead.
If the coil checks out with a fat blue/white spark (never yellow or orange or weak looking) then the Ignition is working. The car battery must be fully charged to 12.6v.
Look for bad cap, rotor, wires, plugs or grossly bad timing of the distributor.
Careful don't get shocked, it hurts REAL BAD.
Test with hands in pockets, or be sorry. Electric shock is not only painful but dangerous, to your heart and can make you jump and get CUT REAL BAD!
Below are drawings of the most common Sidekick ignitions.
If all else fails to make spark, then the ECU is bad. but make sure all power pins on the ECU are at 12vdc, Key On. and all grounds are good.
8v only Power and Ground:
Drawing #1: 8v 91-95 only
OK Success you now have spark from the Ignition coil. So You do have spark, but maybe not at the spark plugs.
Now check spark at each plug.
if you do not have spark at the plugs, then there is only 2 possibilities.:
1: You need a new cap, rotor,wires and plugs ( this is called a tune up and these parts don't last long, 50k miles is a good rating on wires, cap and rotor)
2: The Distributor is mis-Timed grossly.
The below drawings demonstrates the minimum circuits needed to make spark, I may not show the fuses, but it does show battery. You do have power.
Always check spark under load, under the load of spark plug! or dangerous spark flash over can happen, shocking you or damaging the near by electronics parts.
My 8 valve Suzuki Side kick 1991-95, will spark all day long, with only these wires connected: This is called ECU Bench testing.
Drawing 2:
Next trick?
This is called ECU Bench testing.
if your car makes spark and then engine dies, after starting,then the spark filter suppressor is bad. (very rare). its just a 1000-2000 ohm resistor inside.
This device feeds back the spark signals to the ECU ( a monitor watches it) and if missing, kills injection of all fuel, or crash and fire safety.
16 Valve engine (92-95′): Drawing 3:
Note Spark plug connected directly to coil for a true spark test. If this test passes then reconnect distributor center lead and test each of the 4 cylinder plugs for spark.
The 92-98 SOHC 1.6L A new designed Distributor USA: G16 engine.
Note: Hidden COIL (induction)
One can do ECU Bench testing, if you create signals on the white wire the ECU will fire the Igniter transistor and the coil will charge and fire spark.
All you need is power to ECU (& ground) then your white wire pulses and you will see the Orange wire plus (O) called igniter drive.
With this simple diagram one can see how to do the testing, in the light of the above. (a scope at E33 White and E34 Orange will tell all you need)
All they did was move the Igniter to the inside of Distributor along with the COIL. ( the COIL is hidden in the bottle of the Distributor, not the cap)
Note the CMP sensor, does not drive the coil directly and only the ECU can make spark.
Keep in mind, each year 96-98 the ECU is vastly different [software wise ] (thanks to the EPA).
Note that the coil output can not be tested directly, easily, as the older cars could be done. but a test lead can be made up from an old spark wire.
An Alligator clip soldered to spark wire clip, then High voltage spark wire, to its spark boot then boot to tests spark plug. (3 parts) now you can test the coil output)
The Same OBD1, code 41 and code 42 tests work here too from 1992 to 1995 in USA.
Drawing 4:
On this ECU, I only need to make up a CMP HALL type (0-4v pulse) signal generator to pin 3 above. (white) and the bench tested ECU makes park (power wires with power to ECU sure)
The ECU cuts fuel if the brown wire goes dead. (spark read back pin) marked TACHO above. brown wire.
Photo 1: The 1996-98′ CKP sensor. CRANK sensor:
(oddly, it will not prevent starting, but will fail with a DTC code every time. and is used only to make spark more accurate! and for OBD2 misfire monitor, laws)
The EPA mandated this sensor, to the 1996 car and the 8valve TBI engine became illegal here (gone)
It is not a nice HALL sensor, it's just Va R coil sensor, with 2 wire.
Warning: there is no pan gasket, here, starting in 1996, only a RTV glued on pan, if you put a gasket here (as seen in 1995 kits), the CKP goes DEAD (or misfires {far worse that})
The Crank position sensor. USA 1996 and newer. ( the tone wheel is behind the cam cog on crank, it's now part of the cog in 1996)
Click to zoom 96 CKP sensor. Crank position sensor
As you can see the 96+ cars have a Crank Position Sensor CKP (SAE name). ( if it fails, you will get DTC codes for this sensor, and the results my be limphome.) You will fail smog with the CEL glowing for sure.
This device is for the more accurate timing, necessary for the NEW EPA mandated Misfire P030x monitors,of OBD2.
Car will start up, and run, with this device unplugged, but timing will be jittery. (timing belt jitter is real! as all 1995 did. 92-95)
The 96 car does use a CMP (inside the distributor) to make spark, but the CKP above, makes the spark dead accurate, they work together to make perfectly timed spark.
Keep in mind, a loose timing belt will make Misfire DTC's throw and may make this sensor, CKP may show up as bad, when NOT. (think about the cam bouncing madly and the CMP?)
On this OBD2 engine we crank the engine for 5 seconds. With the scan tool attached, and see RPM rise to 300 RPM(about) if not CKP is dead and look for DTC P0340 or P0355 or near.
If the CMP CAM sensor is shown as dead by the ECU scans, the engine will never start.
A dead CKP, the engine will will start, but many OBD2 features, will be inoperative. misfire detection will be dead. (P0300,301, to 304 will be logically DISABLED)
The below CKP is not a Suzuki but is same type and Quality, (ignore the #1 gap pulse below, we don't have that on the G16b) but the signal is 13 times weaker than the CMP at idle.
Cranking the signals will be far lower, (slow moving crank shaft and Faraday's laws win) Only a scope can see this signal, not some Test LED lamp or incandescent lamp, ever.
The signals can be as low as 200mV or 0.2v) while cranking slow in ALASKA. Photo 2: (the below is idling engine, if you speed it up, the signal gets stronger (taller))
On most cars made, if this signal is lost. there will not be spark ever. period. (but not THIS CAR)
Things that can cause CKP to be bad, and not the CKP being bad.
- Wires bad here, end to end. ECU to here (open, shorted, cut, crushed, smashed, rusty, corroded, or mangled)
- Damaged coax on these wires to it., OR no longer grounded at one end this shield, (only) The shield keeps noise off the line. (and needed big time cranking)
- Someone added a pan gasket (fail)
- The ECU is bad, (99.9% sure it's not) Inputs on most ECU never fail. (they are protected is why) but outputs love to fail.
- Someone put a 1992 to 1995 crank cog here, on this engine, with no tone wheel. (engine swaps?)
- Your scope is dead on this channel (LOL). Try channel 2. Test your scope leads, using the test port signal on the scope.
- Using the wrong sensor, or wrong year or off the WRONG CAR.
- If the ECU says its bad, it is. (CKP is bad or the wires, for sure the signal is too weak to read by the ECU)
- The accuracy of the reluctance sensor can also be affected by the sensor magnet attracting particles of ferrous material (from many sources, depends on the 3 common locations that, Front, center,rear of crank)
- If the Cam belt or chain is loose, many ECU will show gross errors with CKP or CMP or both, due to the gross slop of cam and jittering huge of the 2 sensors. (it compares the 2 and sees, omg, what is that bounce there?) BAM DTC errors.
- Watch here the 2000 year 5.7L Chevy 2500 fail to start. The CMP and CKP must align or it drops spark.
- Think about how dumb it would be for the ECU to fire one cylinder, way early,then fire the next way late (a tug of war). (the to pistons rods are going to be stressed hard) question?, why should it? (easy answer) (cuts spark it can)
- To this, add CAM TIMING WAY OFF. (or out of control)
Seems cleaning it first, makes sense, that is, if that act does not destroy the calibration of said sensor, so read the FSM and learn that first, then clean it. (factory serv. manual)
My JEEP must be calibrated, as just one example. (shimmed out) (we use a tape shim) at the flywheel bell mount.
End G16 engine.
1996-1998 1.8Liter DOHC Suzuki Sports. How spark happens? (creation) (and 2.0L and newer and bigger engines.)
OBD2 only USA, cars.See a slide show:
REVIEW:
The new Engines have 2 sensors, to make spark.
The CMP is really 2 sensors in one. It is a high power, 5vdc driver on 2 pins.
The CKP is just crankshaft coil for #1 TDC precision crank positions. (this is a TDC strobe, and is weak 1v signal).
The Engine may run with a dead CKP, like the G16 does, I do not know. But for sure P0300 will happen. and P0335s
When the CMP dies or goes to sleep hot, or misfires, you will get P0340 errors, (DTC)
The FSM clearly states to crank for 10 seconds or run engine for 10 seconds to set these, DTC live or pending errors.
Do not look at the stupid CEL lamp, it's mostly useless, use a real scan too, and do live testing.
These 2 sensors, set the drum beat for the ECU, and it then decides, when and how to make spark, the PCM decides all spark advance, by using tables and live data.
The PCM then fires the COP coils in the firing order 1,3,4,2 (2.0L)
If fuses are good and the COPS are dead, then you need to use a scan tool. You can NOT FIX cars with any CAN TOOL, so buy one for $9 and WIN.
The CKP crank sensor, never fails and is behind the engine, behind the flywheel or A/T flex plate. as seen here. and here.
The CKP and CMP work together, so the ECU can detect P030x misfiring. ( this began in 1996 for all USA OBD2 ECU's)
When any cylinder fires, the combustion causes a very fast acceleration of the crank shaft, all 3 sensors are used to measure this rate of acceleration.
The OBD2 misfire monitor can in fact tell you, which cylinder misfires.
Three thing happen here, injector timing, spark and OBD2 misfire monitoring.
The Fly wheel has holes cut, to make the CKP function. (see slide show above) My V6 2.5L has the same parts. (nearly) only more holes cut in the flex/fly plate.
The ECU will throw codes for failure of either the CKP or the CMP. Or throw DTC P0300 {misfire} or P030n (where n = cylinder failing 1-4)
DO NOT FAIL TO LOOK carefully at the OBD2 scan tools pending DTC fail tables.!!! LOOK.
If the engine does not start?, SCAN it for 5 seconds cranking, IT WILL throw a code, LOOK for it. NOT 1 second, 5!
Scan, crank and look for 5 seconds!!!
If the engine cams, have a loose timing chain, it will throw random misfire codes.
This CMP device likes to fail during HOT restarts (called heat soak fails).
DO NOT remove the CMP at cam rear, with out putting index marks on the base mounts, with a center punch or with scribe markers. 'called match marking'
(on newer, cars 2004 for sure, you need a special scan tool to set ignition timing doing a FREEZE (FIX timing command), Do not mess with the CMP until you have plan!
DO NOT PULL the CMP off the head, on newer cars that have NO TIMING FREEZE JUMPER! (1996 to 2003) Suzuki does have the jumper.
But you CAN, if you mark it very carefully! (scribe it) and win.
IF you can not find DLC2, better have a plan. (like how to time a new sensor).?
The real Suzuki's 1996 to 2004 I think all have a DLC2 connector (at right headlight rear shell or at left strut towner in the engine bay) 6 pins, jumper D to E or 4 to 5, to freeze timing.
The 2000 to 2004 Chevy trackers have no DLC2, and need factory scan tool to set spark timing.
For sure my 2004 DLC2 is missing, (and pray every day, the CMP never fails, now that Suzuki is Chapter 11.)
I got mine scribed, now.
THE CAM SENSOR:
This is the timing spec page. CMP.
CMP signals, both sides (pins) to ground. FSM. 2004
NO Scope CMP tests?:
One can check both outputs of the CMP with any simple analog voltmeter. (per 2004 Vitara 2.0Ll FSM)
Both pins have powerful driver transistors, making the test, easy.
Key on: engine off (emg. brake set, in park or neutral, and wheels chocked)
Nothing disconnected.
Back probing the 4 CMP pins (use a leather sewing needle, to back probe this CMP connector)
Both Pins on the CMP pins 4 is REF and pin 5 is POS, signals, toggle per below: (meter ground lead to engine block metal ground.
Ref. pin 4 toggles 0 to 5v, key on, turning crank slowly by hand, 6 pulses (needle wags) per turn of crank pulley, and see it pulse. (color Y/B)
POS pin 3, toggles just the same, but 360 times per crank turn. easy huh, just a $10 walfart meter and I saved you 200 bucks. (color Y/G)
Pin 2 is 12vdc key on (color BL/B). This the power pin. If 0v the CMP will be dead with no power. (cut wire?)
Pin 1 is 0v key on. it is ECU ground. (color Gr/Y) (0 to 0.5v) of above this the wire is cut or PCM is unplugged.
WATCH OUT, IT LOVES TO FAIL HOT. Sadly as you set up to the these tests, the CMP cools and it starts working. (buy a new one or rebuilt from Cardone for $150)
THE CRANK SENSOR IS NEXT:
Key off, unplug CKP. (rear of block, connector)
The CKP crank sensor is just a 550 ohm mag coil (+/- 100 ohms on CKP pin 1 and 2. (unplugged,) this is just a coil, and has no transistor drivers, like the above, so in this case, only a scope works for a true test. But do use the Ohm meter (resistance) to check pin 1 to 2. (2k ohm meter scale/ range)
If it reads infinity the sensor is bad. (very very rare, this) and takes removing the transmission to replace it.
DTC errors. P0335, if you don't get that DTC, I'd never replace it.
C.O.P'S: 'Coils Over Plugs' or D.I.S (Distributor less Ignition Systems)
No, not the Police! not coppers. 1.8L, 2.0L and bigger,
The 1996 to 2004 USA.
We can have 4 Coils or 6 on a V6 or less (European have wasted spark coil packs (2 in 1 brick).)
COP Ignition COILS. HOW TO TEST COP SPARK IS HERE?
Our V6 has 6 COPS. The USA 1.8L and 2.0L have 4 COP's
Some odd 2 COP wasted spark cars (non USA), are wired is series (HV side), 2 spark plugs fire at once, one on compression and one on exhaust stroke (wasted)
(wasted spark is used on some Kicks, outside of the USA) My 71 Honda CB750 had this long ago, its not a new idea.
(this new system can run.044 ' spark gaps 1999+ only, it is way more powerful that the old generation 96-98 USA Cops that run.028″ gaps)
Again the same tests apply to this engine as the G16B 1996 and newer engines and that is…
On this OBD2 engine we crank the engine for 5 seconds. With the scan tool attached, and see RPM rise to 300 RPM(about) if not CKP is dead and look for DTC P0340 or P0355 or near.
If the CMP sensor is shown as dead by the ECU the engine will never start. A dead CKP, the engine will will start but many OBD2 features, will be inop. misfire detection will be dead.
Dwell Lab Scope Coil Kit
The 1.8Liter Sport: Uses Coil Over Plugs, called a COP.
Aka: Distributor -less – Ignition Systems or DIS.
If you have a dead COP, best way to test it is swap it with on of the other COPS and do a new spark test at each and every COP.
Just lay COP and plug on valve cover and crank and observe.( use a fresh new spark plug to accurate testing)
The 96 -97 COP is different from the 1998 then early COPS had a firewall mounted Igniter transistor block that can fail. (rare for sure)
The 98 COP has the Igniter moved to the inside of the COP coil. do not try to mix COPS from 96/7 to 98 vehicles or you will burn up the ECU.!!
Do NOT.
The Igniters are very reliable. See my tune up page for better photos.
These newest cops fit all Esteems and the 98 fits the 2.0L motor and my 2.5L. the p/n is -77Enn, make sure the nn matches. 98 and newer P/N: 33410-77E21 (cop)
Like regular spark coils the early COPS can be tested just like there former selfs.
a very low resistance primary 0.61-0.73 ohms /
and very high secondary resistance, 2k (2000) to 30k or 30,000 ohms or more. all readings of all coils very by year.! on most Ignition coils but on cops they are way higher.
The COP Igniter transistors were moved into the COP in 1998, deleting the fire wall mounted 4 way Igniter.
96-97 Sport Cops look like this: note the lack of transistors in COP, which means they can be bench tested very easy. (but must be pulsed or they will burn up)
98+ year Cops, see schematic have integrated Igniters, see Schematic here. note the transistors are off, and makes testing primaries very hard.
The test is with a milli-ammeter wired in series with the secondary coil pins. (this forms a crude meg-ohmeter) {most DMM can't do this on any ohm's scale}
A Suzuki method.
'Switch the DVOM to the amp setting, then connect the 12 volt battery and DVOM to the ignition coil as shown in the accompanying illustration to measure the current. The ammeter should register between 0.3-1.4 milliamp. If the current is not within the specified range, replace the ignition coil with a new one.'
Use the 20 milliamp range, on the meter.
Do not power these coils up with a battery only. IT WILL BURN UP FAST!!!
Do not do this with power going through the coil full time or it will burn up the coil. These coils are spec'd out with a very short dwell time.
Only a coil pulser, can test coils live.
Live testing off car:
the 98 COPS are near impossible test unless you want to get shocked. yes it can be done but is a tricky setup, off car.
I say,don't bother trying or risking damage to the COOP,do all COP testing on car, look for fat blue-white spark.
Lay the spark plug (test) on to the valve cover and crank the motor. see the spark? USE NO HANDS!!!
Do not test for spark in the presents of fuel. DE-PRESSURIZE PLEASE.
If the motor is flooded, let it dry overnight with the spark plugs pulled, or crank motor with the fuel pump defeated.
I pull the fuel pump relay and crank the motor dry Wide open throttle. If in a hurry. Then test for spark, free of fuel (safety first)
I check for spark with the spark plugs still in the motor, so this risk is avoided. I use a new spark spark plug, not some old tired shorted plug.
See my Jargon page for 3 letter terms.

